Minimum requirements
In order to user our SDK, you must use it on an Android project with a minSdkVersion at least at API level 23 (Marshmallow 6.0) or higher. To build your own Android's application, we recommend you to use Android Studio as your IDE.
In order to help you with the SDK, you will find an integration example with sources codes :
1. Download our MapSDK
First, you need to download our MapSDK to integrate it in your project :
https://fnoproduction.blob.core.windows.net/sdk/android/1.5.27/20230209__FNOSDK__Android_1.5.27.aar
Ask us a token in order to try our demo through this email : business@findnorder.com
2. Configure your Gradle dependencies
Then you need to go to your build.gradle (Module: app) in order to configure your dependencies :
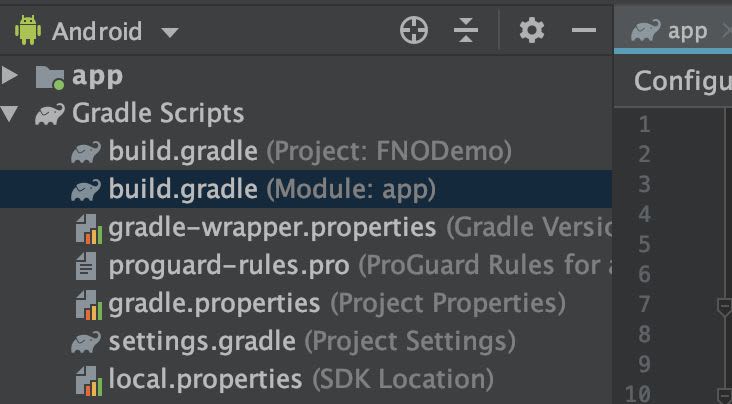
Then in your dependencies block at the bottom of your Gradle file, you need to replace your first line by :
dependencies { implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar', '*.aar']) //If you have other dependencies, please add it below}Adding this line allows you to use your map and our SDK to interact with your map.
3. Add our MapSDK
Then you need to provide your map and our MapSDK in your Android project. In order to do that, switch your file tree in project mode and then place sdk.aar file in the app/libs/directory like this :
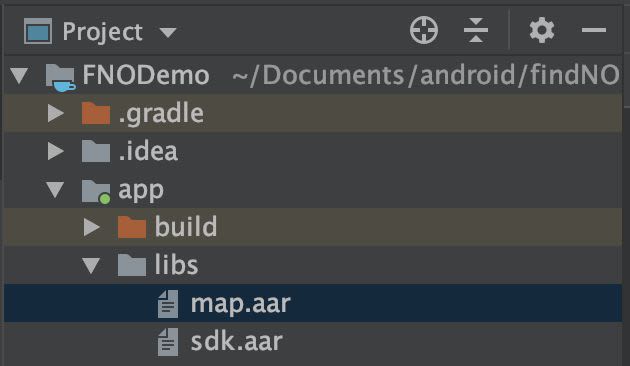
sdk.aar : represents all the methods in order to interact with the map displayed
Once you have added those files in your Android project, you need to refresh it by syncing your Gradle's project files by clicking on this button :

Congratulations! Once synced, our SDK is ready to be used. Now, you need to configure them.
4. Add your client token
When we provide you a map, there are always :
- A client's token
- A map's identifier
Those informations are used to uniquely identified your map and communicates properly with our SDK. So, you need to both in your Android project.
First, go to your values/strings.xml file and add your client's token :
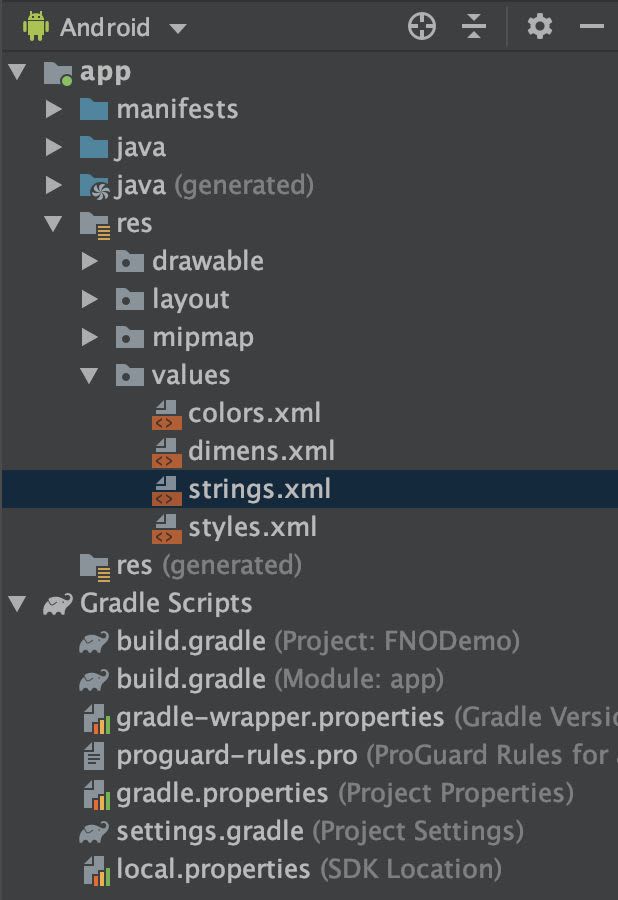
<resources> <string name="client_token">"PUT HERE YOUR CLIENT TOKEN"</string> //If you have other properties, please add it below</resources>You also need to add another line in your values/strings.xml to avoid some errors when loading your map :
<resources> <string name="client_token">"PUT HERE YOUR CLIENT TOKEN"</string> <string name="game_view_content_description">Game view</string> //If you have other properties, please add it below</resources>Now you can access your client's access directly from your values/strings.xml. Now, you need to configure your AndroidManifest.xml.
5. Initialize in your Application and Activity classes
In your Application class:
- Initialize your map by providing your client's token and environment
In your Activity class :
- Start module
- Override
onResumeandonPausemethods
Here is how you can do both :
public class App extends Application { public void onCreate() { super.onCreate(); MapFNO.setEnvironmentForAPI(WebEnvironment.DEV); // PROD by default MapFNO.init("<token>"); } }public class MainActivity extends Activity { public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); MapFNO.startModuleMap(this); } protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); map.onResume() } protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); map.onPause(); } }6. Configure your AndroidManifest.xml
Configuring your AndroidManifest.xml allows you to avoid conflicts with your map and SDK when you compiles your project. So, go to your AndroidManifest.xml :
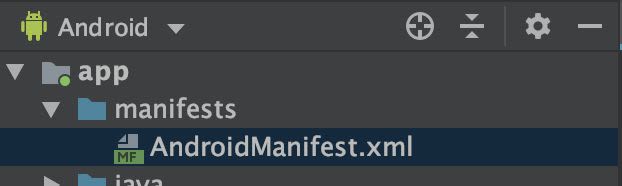
You need to add internet permission and camera permission like this :
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" package="com.fno.demo"> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" /> <uses-feature android:glEsVersion="0x00020000"/> <application //Your other properties </application></manifest>That's it! You are ready to load and display your map and interact with it thanks to our SDK.
7. Load and display your map
A map is represented by the MapFNO's class. To display your map, you need to add a MapFNO's object to your layout :
<findnorder.MapFNO android:id="@+id/map" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" />Then when you set your content view in your activity or fragment, you can retrieve and instantiate your MapFNO's instance. Once you instantiate your MapFNO's instance, you can use the method called displayMapWithId to display your map by passing as a parameter your map's identifier and a callback in order to know when the map is ready to be displayed :
import findnorder.MapFNOpublic class MyActivity extends Activity { private MapFNO map; protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); map = findViewById(R.id.map); map.displayMapWithId("ID_OF_YOUR_MAP", new MapFNO.CallbackLoadMap() { public void onMapReady() { //Interact with your map } }); }}